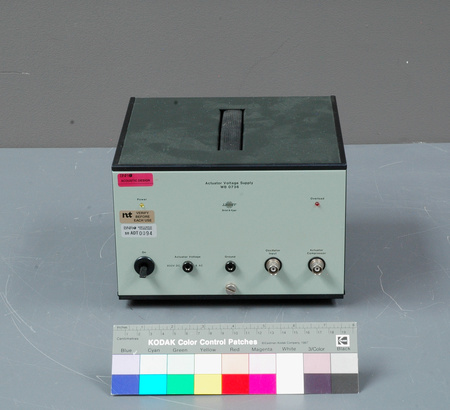
Router
Use this image
Can I reuse this image without permission? Yes
Object images on the Ingenium Collection’s portal have the following Creative Commons license:
Copyright Ingenium / CC BY-NC-ND (Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International (CC BY-NC 4.0)
ATTRIBUTE THIS IMAGE
Ingenium,
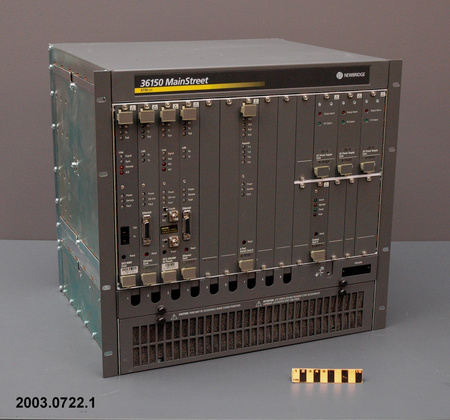
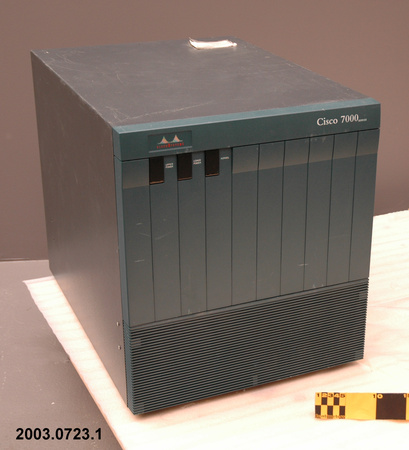
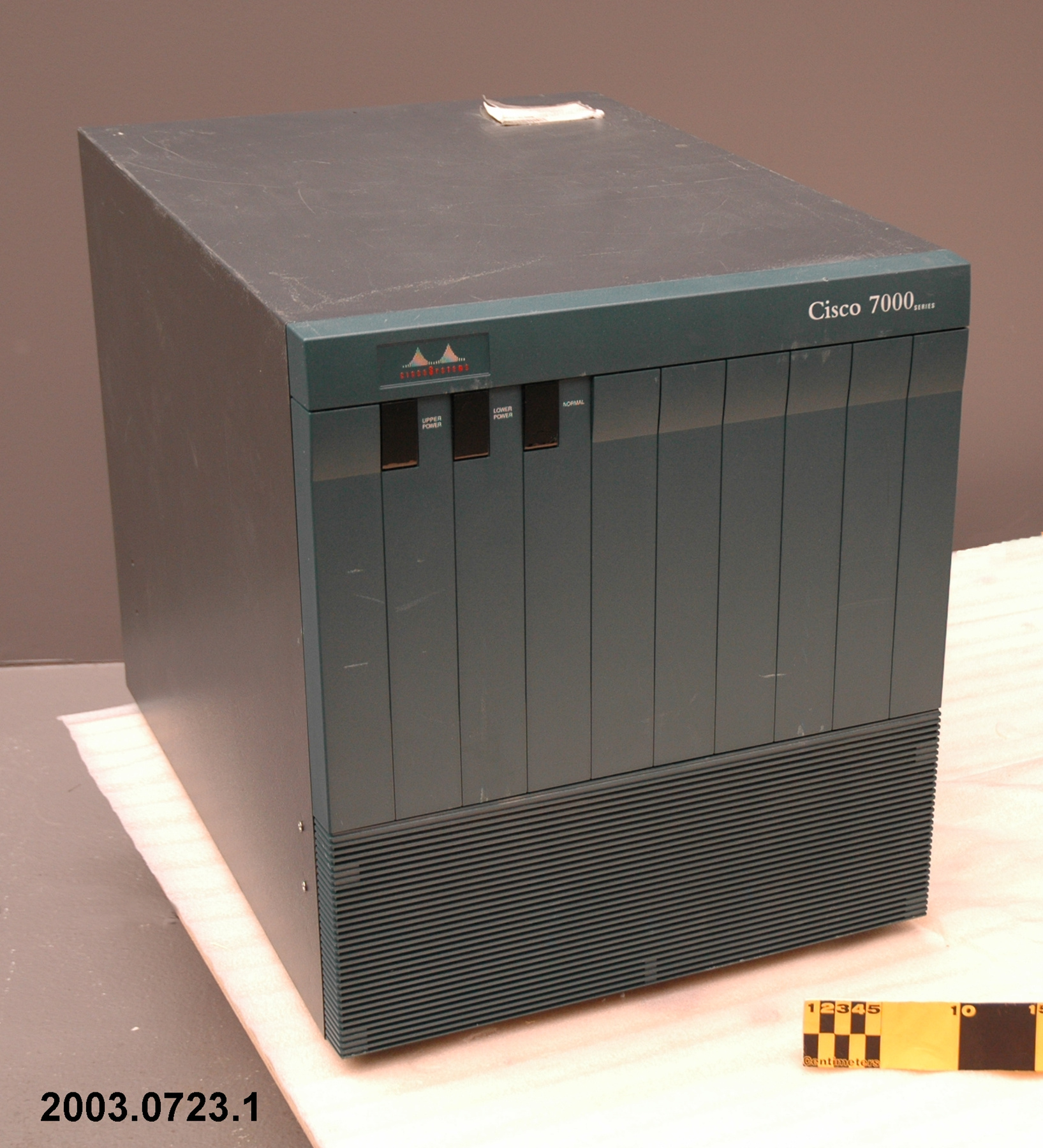
2003.0723.001
Permalink:
Ingenium is releasing this image under the Creative Commons licensing framework, and encourages downloading and reuse for non-commercial purposes. Please acknowledge Ingenium and cite the artifact number.
DOWNLOAD IMAGEPURCHASE THIS IMAGE
This image is free for non-commercial use.
For commercial use, please consult our Reproduction Fees and contact us to purchase the image.
- OBJECT TYPE
- internet protocol
- DATE
- 1995
- ARTIFACT NUMBER
- 2003.0723.001
- MANUFACTURER
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- MODEL
- 7500
- LOCATION
- Menlo Park, California, United States of America
More Information
General Information
- Serial #
- 77010403
- Part Number
- 1
- Total Parts
- 1
- AKA
- N/A
- Patents
- N/A
- General Description
- metal casing with synthetic front panel/ synthetic switches/ metal parts
Dimensions
Note: These reflect the general size for storage and are not necessarily representative of the object's true dimensions.
- Length
- 62.0 cm
- Width
- 44.5 cm
- Height
- 50.4 cm
- Thickness
- N/A
- Weight
- N/A
- Diameter
- N/A
- Volume
- N/A
Lexicon
- Group
- Computing Technology
- Category
- Digital peripheral devices
- Sub-Category
- N/A
Manufacturer
- AKA
- Cisco
- Country
- United States of America
- State/Province
- California
- City
- Menlo Park
Context
- Country
- Canada
- State/Province
- Ontario
- Period
- circa 1995+
- Canada
-
A piece of equipment used by Canadian non-profit corporation Canarie Inc. (Canadian Advanced Network and Research for Industry and Education) in its nation-wide advanced computer networks. CANARIE Inc., based in Ottawa, is Canada's advanced network organization. It facilitates the development and use of its network as well as the advanced products, applications and services that run on it. The CANARIE Network serves universities, colleges, schools, government labs, research institutes, hospitals and other organizations in a wide variety of fields in both the public and private sectors. By promoting and participating in strategic collaborations among key sectors, and by partnering with peer networks and organizations around the world, CANARIE Inc. stimulates and supports research, innovation and growth, bringing economic, social, and cultural benefits to Canadians. The national organization was created in 1993 by the private sector and academia under the leadership of the Government of Canada. CANARIE Inc. is supported by membership fees, with major funding of its programs and activities provided by the Government of Canada through Industry Canada. The original CAnet was created in 1990 with support from the National Research Council. Its purpose was to provide Internet connectivity between universities and research organizations in Canada, with connections to similar networks in other countries. That initiative and the organizations that took part in it were the pioneers of the Internet in Canada. CAnet 4 is the latest version to be implemented In the fall of 1995, the National Test Network, or NTN, was launched, also in partnership with Bell Advanced Communications (BAC), along with AT&T Canada and Teleglobe Canada. It was one of the first national ATM networks in the world. In combination with the various regional test networks then being deployed, it was arguably the largest ATM research and test network in the world at that time. The focus of the network was on basic ATM experimentation and ATM applications, and access to the network was limited to specific researchers and specific labs located at universities and other research facilities across the country [Ref. 1]. - Function
-
A data transmission component of a computer network that forwards blocks of data or packets from one network to another. - Technical
-
The Cisco 7000 series router was a piece of technology that played a major role in the expansion of internet services in the 1990s. "The key to these carriers' [Pacific Bell and MCI] Internet services rollout was the Cisco 7000 Series Router, first introduced in 1993. While the Cisco Advance Gateway Server (AGS) gave birth to the Internet, it was the Cisco 7000 Series that gave it its legs. It could forward 110,000 packets-per-second, and boasted several much-requested features that boosted reliability, availability, and serviceability, including redundant power, hot-swappable line cards, and flash memory-based storage to easily update software images. More important than its speed was its ability to make a wide variety of networking work. A common early application, for example, was connecting corporate local-area networks with Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) cell-switching backbones. [See 2003.0772] The increasing demand for Internet access caused customers to demand more speed and capabilities. In response, Cisco introduced the first multi-gigabit backplane router in 1995: the Cisco 7500 Series. The new routers expanded bandwidth capacity by four times, provided redundancy for route/switch processing, and increased maximum port density by 100 percent. The Cisco 7500 Series also provided a significant upgrade in network capacity, including high-speed switching, gigabit LAN, and Synchronous Optical Network (SONET) technologies. It eventually became a multifaceted workhorse for corporate environments, supporting Ethernet, Token Ring, Fast Ethernet, Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI), high-speed serial interface, ATM, E1/T1, and even IBM channel attachments. Scalable system bandwidth exceeded two gigabits per second (Gbps), resulting from a new, multiprocessor architecture with several innovative elements. The first element was the Cisco 7500 Route/Switch Processor (RSP). Using a high-speed Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) engine and custom application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs), the RSP speeded route and switch processing. Dual-RSP configurations maximized system and application availability. Another innovation was a new Versatile Interface Processor (VIP) card. The VIP was the first router interface card to provide intelligent multilayer switching and run Cisco IOS® Software. By making local switching decisions, based on routing information received from the RSP, VIP cards enabled users to switch packets at aggregate rates greater than one million packets-per-second. Another important VIP card innovation was the concept of modular interfaces. ]Continued in Notes]. - Area Notes
-
Unknown
Details
- Markings
- white lettering on front reads 'Cisco 7000/ SERIES'/ red and white logo on front reads 'CISCO SYSTEMS'/ lettering on label on back reads in part 'Cisco Systems Inc./ 1525 O'Brien Drive/ Menlo Park, CA 94025 U.S.A. MADE IN U.S.A.'/ white barcode label on back reads '77010403'/ red letterin on back reads 'CISCO SYSTEMS INS./ MENLO PARK, CA, MADE IN U.S.A.'/ label on back reads 'CANARIE/ RNET'/ label on back reads 'SOLD BY BELL CANADA/ VENDU PAR BELL CANADA'/
- Missing
- appears complete
- Finish
- dark grey painted textured casing with teal blue synthetic front panel/ black synthetic switches/ plated parts
- Decoration
- N/A
CITE THIS OBJECT
If you choose to share our information about this collection object, please cite:
Cisco Systems Inc., Router, after 1995, Artifact no. 2003.0723, Ingenium – Canada’s Museums of Science and Innovation, http://collection.ingenium.ca/en/id/2003.0723.001/
FEEDBACK
Submit a question or comment about this artifact.
More Like This